Técnica de Lipoescultura Facial
No contexto dos tratamentos estéticos faciais,
a lipoaspiração ou lipoescultura cervicofacial (LE) se destaca,
pois remove suavemente células do tecido adiposo (AT),
esculpindo com precisão os depósitos indesejados de AT no rosto e pescoço [1-3].
Em 2020, cerca de 15,5 milhões de procedimentos estéticos
foram realizados somente nos Estados Unidos,
de acordo com o relatório de 2018 da The Aesthetic Society [1].
Nesse cenário, foram feitas otimizações nas
técnicas de suspensão do sistema músculo-aponeurótico superficial
e dos coxins de gordura adjacentes [2,3].
Procedimentos minimamente invasivos em LE facial estão em expansão,
resultando em efeitos estéticos ideais [3-5].
No entanto, como é tecnicamente desafiador remover
uniformemente os depósitos subcutâneos de AT com técnicas abertas,
essas tentativas muitas vezes produzem contornos irregulares da pele.
Nesse sentido, as técnicas de contorno com lipo oferecem
uma forma de modelar os depósitos de AT do pescoço e rosto
para alcançar melhor o perfil facial desejado [6].
Portanto, a LE é uma alternativa para o rejuvenescimento facial
que envolve a pele, a liberação dos ligamentos de sustentação
e a remoção adequada do tecido adiposo da camada subcutânea,
enquanto melhora o tônus da pele e o contorno facial.
Para corroborar isso, um estudo clínico observacional
com 312 pacientes submetidos ao rejuvenescimento cervicofacial
mostrou os benefícios da lipoescultura nesse tipo de rejuvenescimento,
em termos de redução das rugas de marionete,
remoção do volume perioral, contorno facial em “V”, mandíbula definida,
redução da papada, projeção visual do queixo e lifting cervicofacial [7].
Assim, o presente artigo teve como objetivo apresentar e
registrar as técnicas de otimização da lipoescultura facial
como uma importante ferramenta estética para o cirurgião-dentista.
Protocolos – Técnicas de Lipoescultura
Estado da Arte da Técnica de Lipoescultura Facial
A ideia da técnica surgiu para resolver os problemas relacionados às alterações nos coxins de gordura da face que ocorrem ao longo dos anos e com o envelhecimento (Teoria do Volume).
Sabendo que o rosto possui compartimentos de gordura que mudam de tamanho com a idade e o ganho de peso, o objetivo é reestruturar funcionalmente a superfície desses coxins de gordura, sem rompê-los.
Anatomicamente, o trabalho é feito na superfície dos coxins, entre a derme e o SMAS (Sistema Músculo-Aponeurótico Superficial), remodelando seu volume ou até redesenhando esses coxins, caso seja anatomicamente necessário, para proporcionar uma aparência mais jovem ao rosto, uma expressão mais leve ou até mesmo modificações nas características étnicas.
Também é possível tratar rostos irregulares e malformados que apresentam alterações funcionais nos coxins de gordura. Assim, o principal objetivo é corrigir a funcionalidade do aparelho estomatognático que se modificou ao longo do tempo e que pode interferir em seu funcionamento — e, como consequência, alcançar um resultado estético significativo.
Rostos muito arredondados ou sem contorno no terço médio da face, que muitas vezes levavam à escolha da bichectomia como técnica para redesenho estético, hoje são tratados com lipoescultura facial, preservando a integridade local da bola de Bichat, que é tão valiosa como amortecedor e lubrificante entre os músculos faciais. Além disso, por ser uma fonte rica em células-tronco mesenquimais indiferenciadas, manter a bola de Bichat intacta é uma opção para futuras terapias celulares.
Portanto, a técnica foi desenvolvida com rigoroso embasamento anatômico e funcional.
Técnica – Abordagens Principais
A própria técnica consiste em remodelar os coxins de gordura superficiais da face para restaurar o design perdido ao longo dos anos ou por ganho de peso.
A Teoria Volumétrica nos diz que esses coxins saem de posição e aumentam de volume, e esse aumento faz o rosto parecer envelhecido.
Se falta definição no contorno, é preciso remodelar esses coxins antes de qualquer técnica de harmonização orofacial. Antes, usavam-se técnicas de preenchimento e fios de sustentação. Essa tração por fios nos coxins deslocados não é muito eficaz, porque, devido ao peso — segundo a Teoria Volumétrica —, eles não se mantêm na posição puxada pelos fios por muito tempo.
A técnica de Lipoescultura Facial foi criada exatamente para redefinir esses rostos “pesados”. Como não havia instrumentos específicos, desenvolvemos toda a linha com a empresa Supremo Instrumentais. Os instrumentos que assino foram projetados com características pensadas na segurança e na qualidade do design proporcionado pela técnica.
Técnica Passo a Passo
Para a excelência de qualquer técnica, o planejamento técnico é fundamental. Por isso, hoje o desenho do rosto do paciente é planejado em detalhes, levando em consideração as áreas anatômicas que precisam ser redesenhadas — considerando estruturas ósseas, cutâneas e musculares.
A lipoescultura é, de fato, como o nome indica: uma escultura de gordura, sendo todo o trabalho realizado na superfície dos coxins, sem qualquer preocupação quanto à sua integridade estrutural, pois estes são preservados.
Após o planejamento inicial, é realizada uma avaliação clínica minuciosa, tanto visual quanto por palpação, para analisar as características da gordura, volumes e estruturas anatômicas locais. Todas as particularidades de cada paciente são consideradas.
Essa é a fase de planejamento que leva em conta as fisiologias cronológicas que se deseja alcançar, com o objetivo de proporcionar uma aparência mais jovem e reposicionar os tecidos.
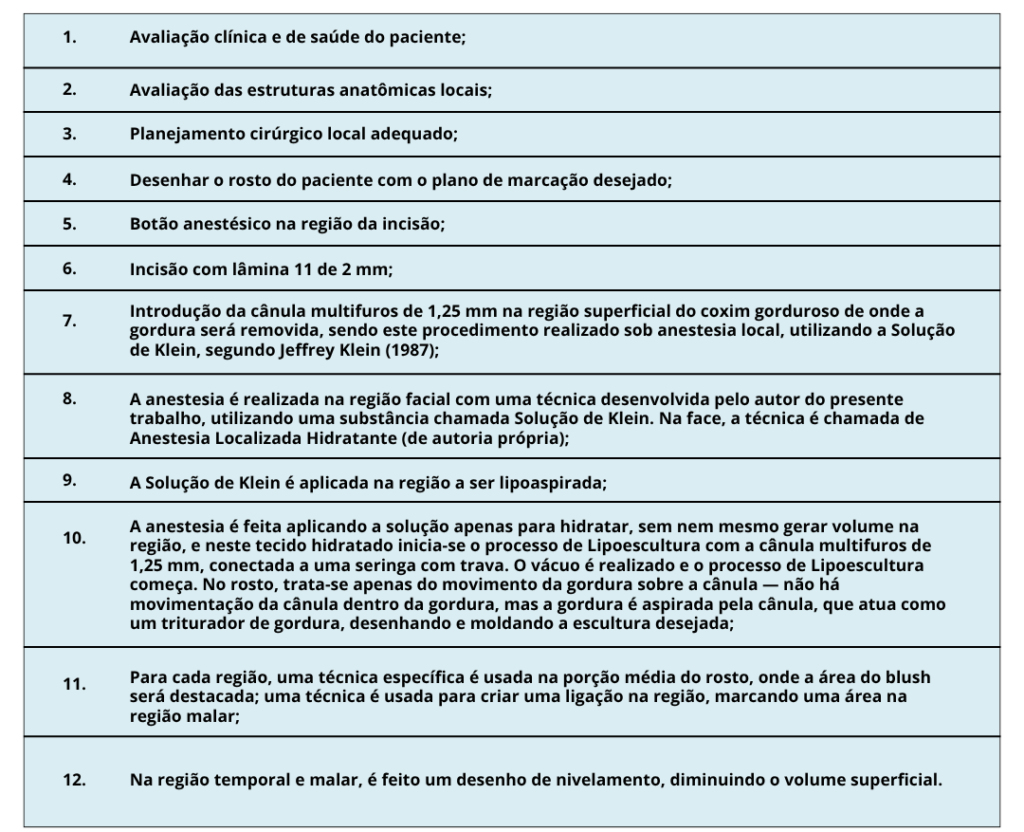
Assim, dentro do planejamento do design a ser executado, o passo a passo está apresentado na Tabela 1.
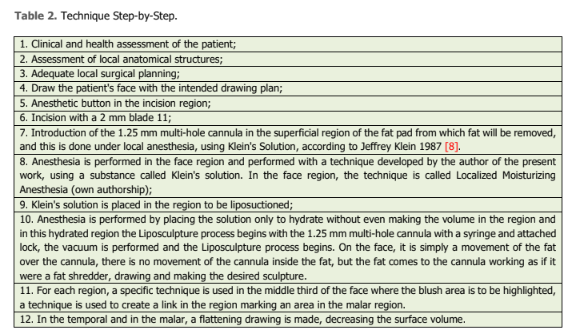
Tabela 1. Técnica passo a passo.

Na região da face, uma cânula multifuros de 1,25 polegadas é utilizada para esculpir e, na área do blush, finalizamos a curvatura do desenho próximo à região nasal, com a cânula curva multifuros de 1,25 polegadas (desenvolvida pelo autor do presente trabalho, de forma que se possa fazer o mesmo nível de curvatura do desenho da face em ambos os lados).
A incisão na região do trago é realizada com lâmina 11, a 5 mm à frente do trago. Por esse mesmo trajeto estreito, também é possível acessar a região malar média e medial, onde alguns pacientes apresentam volumes excessivos ou deformados.
A técnica de acesso à região temporal também é feita pelo trago, e o trabalho sobre essa superfície almofadada é mais delicado, porém seguro, pois é sempre realizado ao nível da gordura subcutânea, com pinçamento e tração da gordura afastando-a do SMAS, onde estão localizadas todas as estruturas nobres, e nessa área deve-se estar atento ao movimento delicado, já que há uma artéria temporal superficial que passa ao nível e é protegida pelo SMAS.
O que torna a técnica segura é o fato de que atualmente temos instrumentos específicos para a região da face, que são bastante delicados e não necessitam de movimentação da cânula dentro da gordura como é feito em regiões com maiores volumes de gordura. Na região da face, há o movimento da gordura sobre a cânula, sem o menor movimento brusco da cânula. Isso torna a técnica muito segura. Claro, o profissional precisa ter excelente formação técnica e científica. Outras regiões da face podem ser aspiradas, mas exigem diferentes pontos de entrada para a cânula.
Na revisão do coxim gorduroso nasolabial, é necessário fazer um trajeto estreito em seu alinhamento, que é transversal ao trajeto estreito da região do trago.
Assim, especialmente para esse coxim, é feito um trajeto estreito na direção da comissura labial com uma agulha 18 G, e a partir disso, a superfície desse coxim é nivelada, deixando-os mais leves e conferindo um aspecto mais jovem ao rosto.
Na região do coxim gorduroso da pálpebra inferior, também é necessário fazer um trajeto estreito diferenciado. Na região de evocação, 10,0 mm para fora e 10,0 mm para baixo, realiza-se o trajeto estreito para acessar o coxim gorduroso da pálpebra inferior de forma paralela, removendo assim os excessos da superfície desse coxim.
Técnica de Lipoaspiração (Lipoescultura)
A técnica de lipoaspiração, também chamada de Lipoescultura, consiste na utilização de uma cânula com motor acoplado para aspirar essa gordura, exatamente como é feito na cirurgia plástica, ou com uma seringa com trava conectada.
Utiliza-se a seringa de 20 mL com trava.
Quando a trava é puxada com o êmbolo da seringa, cria-se um vácuo (pressão negativa) dentro dessa seringa, portanto, em toda a região da face, trabalha-se com a seringa e a trava, sem motor.
O uso do motor para aspiração é permitido apenas nas regiões submentoniana e submandibular, que são regiões com maiores volumes de gordura, onde a segurança permite esse uso.
O segredo da técnica de Lipoescultura Facial (SV LipoSuction Face) é que ela trabalha sempre com pinçamento da gordura e aspiração com seringa, tornando a técnica mais segura e menos traumática.
Com as técnicas faciais, é possível acessar toda a face do paciente para revisões e escultura com total segurança e previsibilidade, sem necessidade de internação hospitalar, com baixa morbidade, alta segurança, sem cicatrizes, com previsibilidade e resultados muito satisfatórios de um redesenho em uma única sessão.
Na região da base da mandíbula, utiliza-se a técnica de trajeto estreito na região abaixo do queixo (2,0 mm após a estrutura óssea), inicialmente com lâmina 11, de 22,0 mm de comprimento, e com a cânula multifuros de 2,5 mm, para realizar o desenho da base da mandíbula com total segurança às estruturas anatômicas complexas que passam nessa região (artéria e veia facial, glândula submandibular, nervo facial), já que a cânula também foi projetada para fragmentar a gordura sem necessidade de movimentar a cânula, apenas a gordura é aspirada por uma seringa de 20 mL.
Hoje, é possível desenhar todo o rosto com total segurança, pois, além das cânulas específicas, existem protocolos muito rigorosos de manuseio da gordura, destacando-a do SMAS e trabalhando o redesenho longe dos planos profundos.
Claro, qualquer técnica exige treinamento intensivo e protocolos rigorosos, por isso foi desenvolvido um passo a passo para atingir resultados de satisfação e conforto ao paciente.
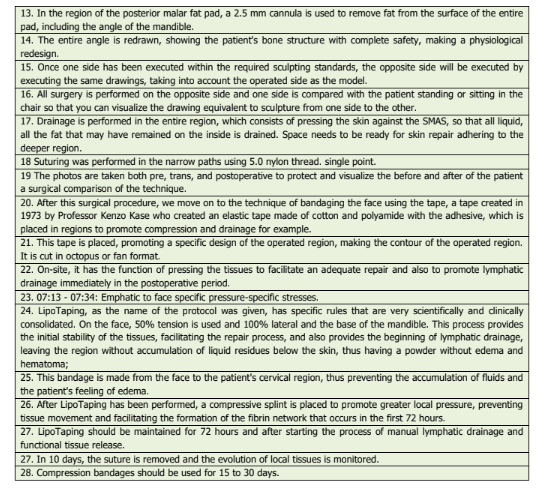
O passo a passo dessa técnica está listado a seguir (Tabela 2).

Facial Liposculpture Technique
In the context of facial aesthetic treatments,
cervicofacial liposuction or liposculpture (LE) stands out,
which gently avulses adipose tissue (AT) cells,
accurately sculpting unwanted AT deposits on the face
and neck [1-3]. In 2020, about 15.5 million cosmetic
procedures were performed in the United States alone,
according to The Aesthetic Society’s 2018 report [1].
In this scenario, optimizations have been made in
the techniques of suspending the superficial
musculoaponeurotic system and the adjacent fat pads
[2,3]. Minimally invasive procedures in facial LE are
expanding, resulting in optimal esthetic effects [3-5].
However, as it is technically challenging to remove
subcutaneous AT deposits evenly with open techniques,
these attempts often produce uneven skin contours. In
this regard, lipo contouring techniques provide a means
to shape the AT deposits of the neck and face to better
obtain the desired facial profile [6].
Therefore, LE is an alternative to facial
rejuvenation that involves the skin, release of the
retaining ligaments, and appropriate removal of adipose
tissue from the subcutaneous layer, while improving
skin tone and facial contour. To corroborate this, an
observational clinical study with 312 patients
undergoing cervicofacial rejuvenation showed the
benefits of liposculpture in cervicofacial rejuvenation in
terms of reduction of marionette wrinkles, perioral
mound removal, V-shaped facial contour, defined jaw,
reduced double chin, visual chin protrusion, and
cervicofacial lift [7].
Therefore, the present article aimed to present and
register the facial liposculpture optimization techniques
as an important aesthetic tool for dental surgeon.
Protocols – liposculture techniques
State of the Art of Facial Liposculpture Technique
The idea of the technique arose to solve the
problems of changes in the fat pads of the face that
occur over the years and with age (Volume Theory).
Knowing that the face has fat compartments and these
change in size with age and weight gain. The objective
is to functionally restructure the surface of these fatty
pads, without disrupting them.
Anatomically, we work on the surface of the
cushions, between the dermis and the SMAS (Superficial
Musculo-Aponeuro¬t¬ic System) remodeling it in
volume or even redesigning the cushions if anatomically
necessary to give a more youthful appearance to the
face, or a lighter appearance, or even changing ethnic
characteristics.
It is also possible to treat bumpy and malformed
faces that have functional alterations of the fat pads.
Thus, the main objective is to correct the functionality
of the stomatognathic apparatus that has changed over
time and that may interfere with its functioning, and as
a corollary of this a significant aesthetic achievement.
Faces very rounded or without contours in the
middle third of the face and that we often chose to do
the bichectomy as a technique that provides the
aesthetic redesign of the face, today we do facial
liposculpture and maintain the local integrity of the
bichat ball that is as valuable as damper and lubricator
between facial muscles. And even as it is a huge source
of undifferentiated mesenchymal cells, keeping the
bichat ball intact is an option for future cell therapy.
Therefore, the technique was based with considerable
rigor on anatomical and functional study.
Technique – Main Approaches
The technique itself consists of remodeling the
Sciences surface fat pads of the face in order to restore the lost
design over the years and or weight gain. The
Volumetric Theory tells us that with fat pads they get
out of position and increase in volume and this increase
in volume makes the face look aging.
If there is an aspect of lack of definition in the
design, then it is necessary to remodel these fat pads
before any orofacial harmonization technique. Before,
filling techniques and support thread techniques were
used. This traction by support threads for the fatty pads
that have come out of position, is not very effective for
repositioning, because due to the weight, which the
volumetric theory tells us, it does not stay in the traction
position by the thread for a long time due to the weight.
The Facial Liposculpture technique was created
exactly to reshape these heavy faces. As there were no
specific instruments, so we created the entire line with
the company Supremo instrumentals. The specific
instruments on which I sign for him were developed
with features designed for the safety and quality of the
design provided by the technique.
Technique Step-by-Step
For the excellence of any technique, technical
planning is paramount, so today, the patient’s face
drawing is planned in detail, taking into account the
anatomical areas to be redrawn. Taking into account the
bone, skin, muscle anatomical structures. Liposculpture
work really is as the name says, a fat sculpture being
the whole work performed on the surface of the pads
without the slightest concern, as the pads are
structurally preserved.
After the initial planning, a clinical evaluation is
carried out in a thorough, visual and handling way to
evaluate the characteristics of the fat, volumes, local
anatomical structures. All the peculiarities of each
patient. It is the planning phase that takes into account
the chronological physiologies that you want to achieve
in order to give a more youthful appearance and in order
to reposition the tissues. Thus, within the planning of
the design to be executed, the following step-by-step is
shown in Table 1.

In the face region, a 1.25-inch multihole cannula
is used to sculpt and in the blush area, we finish the
curvature of the design close to the nasal region, with
the 1.25-inch curved multihole cannula (developed by
the author of the present work, in such a way that it can
be if you make the same level of curvature of the face
design on both sides).
The incision in the tragus region is performed with
a blade 11 and 5 mm in front of the tragus. Through
this same narrow path, it is also possible to access the
medial and medial malar region, where some patients
have excessive or deformed volumes.
The technique for accessing the temporal region is
also performed by tragus and the work on this
cushioned surface is more delicate but safe, as it is
always worked at the level of subcutaneous fat and with
pinching and pulling the fat away from the SMAS, where
they are located. all noble structures, and in this area
one is attentive to the delicate movement, as there is a
superficial temporal artery that passes at the level and
is protected by the SMAS.
What makes the technique safe is the fact that we
currently have specific instruments for the face region,
which are quite delicate and do not need to move the
cannula inside the fat as is done in regions with greater
volumes of fat. In the face region, there is the
movement of fat over the cannula, without the slightest
sudden movement of the cannula. This makes the
technique very safe. Of course, the professional needs
excellent technical and scientific training. The other
Sciences regions of the face can be aspirated, but they require
different points of entry for the cannula.
In the revision of the nasolabial fat pad, it is
necessary to make a narrow path in its alignment, which
is transversal to the narrow path in the tragus region.
So, especially for this cushion, a narrow path is made in
the direction of the labial commissure with an 18 G
needle, and from this, the surface of this cushion is
flattened, leaving them lighter and giving a younger
face feature.
In the region of the fat pad of the lower eyelid, it
also needs to make a differentiated narrow path. In the
evocation region, 10.0 mm outwards and 10.0 mm
downwards, the narrow path is carried out to access the
fat pad of the lower eyelid in a parallel way, thus
removing excesses from the surface of this pad.
Liposuction Technique (Liposculpture)
The liposuction technique, also called
Liposculpture, consists of using a cannula with the
motor attached to suck this fat exactly as it is done in
plastic surgery or with a syringe and lock connected.
The 20 mL syringe with a lock.
When the lock is pulled with the syringe plunger,
it creates a vacuum (negative pressure) inside this
syringe, so in the entire face region, we work with the
syringe and the lock without a motor. The use of the
motor for aspiration is only allowed in the submental
and submandibular regions, regions with larger volumes
of fat where safety allows this use.
The secret of the Facial Liposculpture technique
(SV lipoSuction Face) is that it always works with fat
pinching and a syringe for aspiration, thus making the
technique safer and less traumatic.
With face techniques, it is possible to access the
entire face of the patient, for reviews and sculpting with
total safety, and predictability, without the need for
hospital admission, with low morbidity, high security,
without scars, with predictability and very satisfactory
results of a redesign in a single query.
In the mandible base region, the narrow path
technique is used in the region below the chin (2.0 mm
after bone structure), initially with an 11.0 blade of 22.0
mm in length and with the 2.5 mm multihole cannula,
the design of a base of the mandible with complete
safety the complex anatomical structures that pass in
this region (facial artery and vein, submandibular gland,
facial nerve), as the cannula was also designed to break
up the fat without the need to move the cannula, but
only the fat which is aspirated by a 20 mL syringe.
Today it is possible to design an entire face with
total security because in addition to specific cannulas,
there are very strict protocols for handling the fat,
highlighting the same from the SMAS, and working the
redesign away from the deep planes. Of course, any
technique wants intensive training and rigorous
protocols, which is why a step-by-step approach was
developed to achieve patient satisfaction and comfort
results. The step-by-step of this technique is listed
below (Table 2).